LPIS Implementation
Tables in the database#
Land Table#
CREATE TABLE `land` (
`id` bigint NOT NULL,
`identificator` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL,
`pa_description` text,
`wkt` text,
`wgs_geometry` mediumtext,
`wgs_max_lat` float DEFAULT NULL,
`wgs_min_lat` float DEFAULT NULL,
`wgs_max_lng` float DEFAULT NULL,
`wgs_min_lng` float DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb3;
- id - identifier of shape
- identificator - shape identifier which will be shown in the center of shape
- pa_description - additional Paying Agency (PA) description of the shape
- wkt - definition of shape in WKT format(optional)
- wgs_geometry - JSON array, definition of shape points in WGS84 (mandatory)
- wgs_max_lat - max latitude coordinate in WGS84 (mandatory)
- wgs_min_lat - min latitude coordinate in WGS84 (mandatory)
- wgs_max_lng - max longitude coordinate in WGS84 (mandatory)
- wgs_min_lng - min longitude coordinate in WGS84 (mandatory)
An example of the WKT polygon#
POLYGON((-654859.1 -1032055.2, -654857.0212 -1032074.0922, -654853.4228 1032101.6089,
-654850.3537 -1032116.7431, -654848.6603 -1032121.294, 654737.0059
-1032162.7807, -654667.601 -1032189.0472, -654613.8552 1032209.2262,
-654562.2437 -1032229.2111, -654561.5 -1032192.3, -654557.073
-1032155.2489,
-654553.1925 -1032133.4648, -654550.282 -1032122.3523, 654558.3631
-1032118.8091, -654668.183 -1032078.4512, -654758.2121 - 1032043.5261, -654844.2 -1032012.6, -654862.7 -1032007.1, -654863.2 1032012.6,
-654862.5 -1032027, -654859.1 -1032055.2))
An example of the WGS geometry#
wgs_geometry – [[[50.28668701440919,15.622964665615962],
[50.286520655841976,15.623025546347007],
[50.286278970421144,15.623122167334028],
[50.28614722331331,15.623190491389659],
[50.28610844072792,15.623221769426197],
[50.28585904892955,15.624847153130938],
[50.28569974686514,15.625858298467003],
[50.28557781974232,15.626641032658297],
[50.285455310124476,15.627393705490126],
[50.285785541616185,15.627341724108128],
[50.28612100838588,15.627340812470965],
[50.286319627802456,15.627358073799163],
[50.28642195493316,15.627379847466681],
[50.286444832616766,15.62726129584505],
[50.28668616901868,15.625663366092011],
[50.28690042068134,15.624350280454227],
[50.28708334256413,15.623100233584381],
[50.287112399796946,15.622833238526974],
[50.28706277205572,15.622835567713164],
[50.28693501278767,15.622869652039054],
[50.28668701440919,15.622964665615962]]]
}
Map EGNSS4CAP#
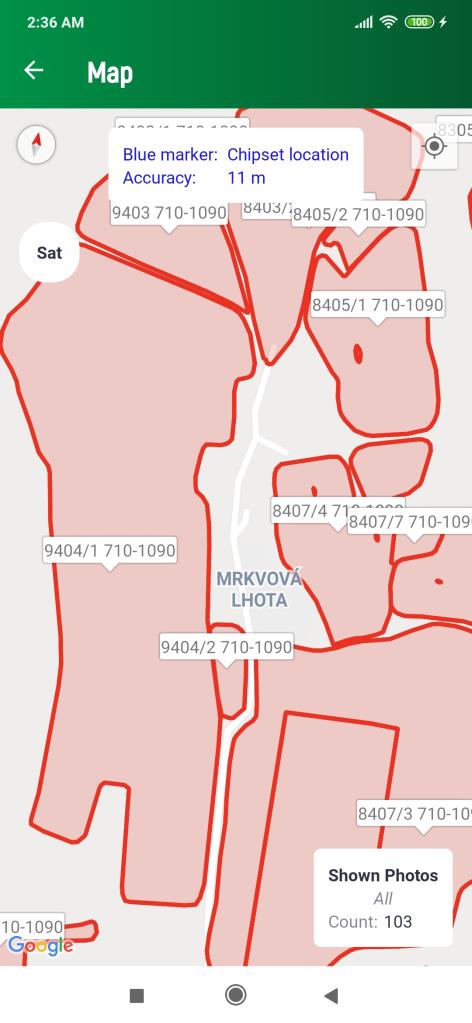
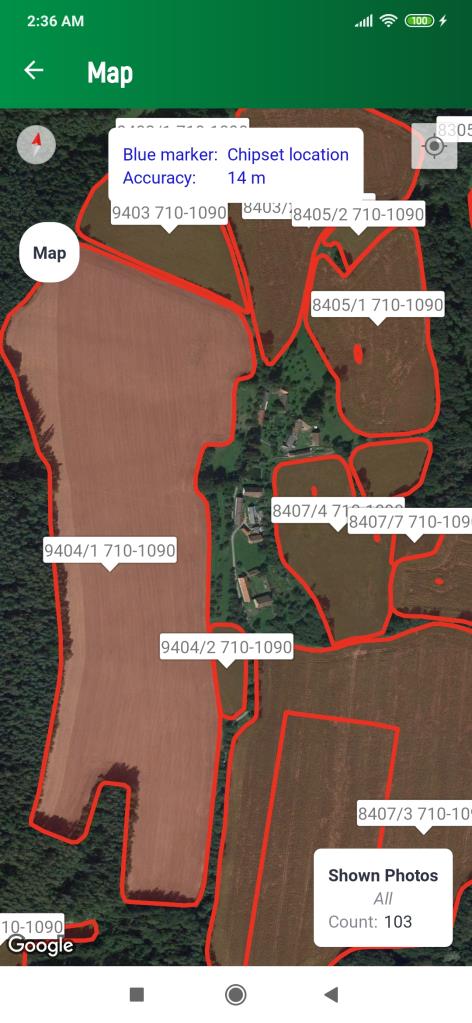
With a sufficiently large zoom above the map in both modes, plots with their identifiers will begin to appear as red polygons. This LPIS rendering is currently only possible for the territory of the Czech Republic, and depends on the availability of LPIS data per EU Member State.
There is a black dot in the photo mode of the map at the location where the image was taken, with a small icon above it. The green circle determines the azimuth direction of the mobile device's screen at the time the photo was taken. Press the image icon to display an overview of the basic attributes of the image. If it is a photo within a task, pressing this report will take the user to the detail of the task to which the image belongs. (Fig. 13). In the photo mode of the map, a window with information about the type of displayed photos and their total number is displayed in the lower right corner. Clicking in this report will move the map view to all these photos.
Further information#
-
LPIS is stored in db table named land. One shape is saved as one row, described by JSON array of WGS84 coordinates. This could also be described by WKT format.
-
To import Land Parcel Identification System (LPIS) data, an import of new shapes into the land table is necessary.
af:LU.ExistingLandUseObject_LPIS_2023, af:LU.ExistingLandUseObject_LPIS_2024, bu:BU.Building, bu:BU.Building_PCN, su:SU.AreaStatisticalUnit,
Map with parcels displayed
OGC API - Features#
This GitHub repository contains OGC's multi-part standard for querying geospatial information on the web, "OGC API - Features". All approved versions of the specification can be found here.
OGC API standards define modular API building blocks to spatially enable Web APIs in a consistent way. OpenAPI is used to define the reusable API building blocks with responses in JSON and HTML.
The OGC API family of standards is organized by resource type. OGC API Features specifies the fundamental API building blocks for interacting with features. The spatial data community uses the term 'feature' for things in the real world that are of interest.
If you are unfamiliar with the term 'feature', the explanations on Spatial Things, Features and Geometry in the W3C/OGC Spatial Data on the Web Best Practice document provide more detail.
Overview#
OGC API Features provides access to collections of geospatial data.